Contents

Space X, Falcon9:
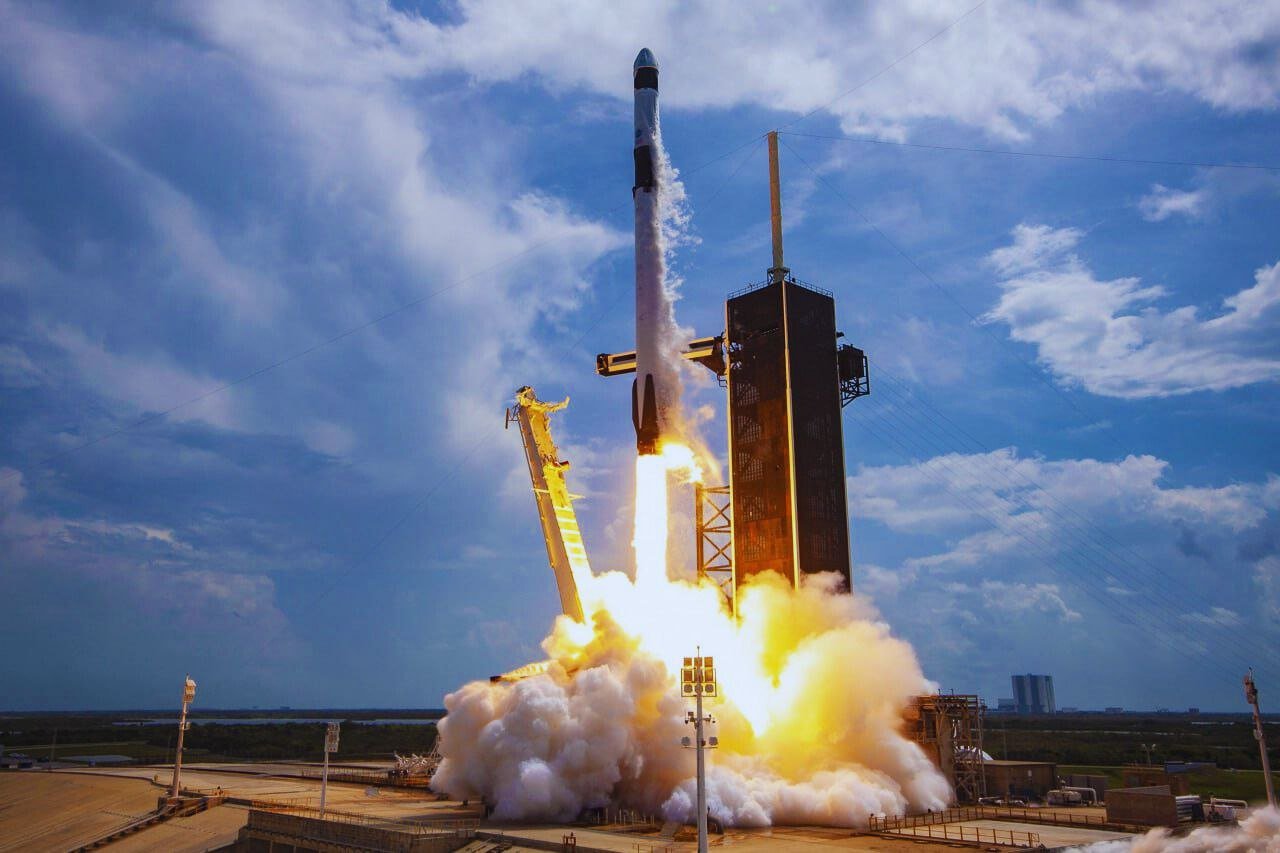
The important launch of a series of espionage satellites for the US government by SpaceX, a private aircraft manufacturer and space transportation business. Early on Wednesday morning, the Vandenberg Space Force Base in California conducted the launch. The National spy Office (NRO), which is in charge of running US spy satellites, carried out the operation, designated NROL-146.
About the particular payloads that the NROL-146 mission is carrying, not much is known. This lack of detail is typical of NRO missions, as the organisation prefers to keep the actions and capabilities of its satellites secret. As a result, no film of the stages of the Falcon 9 rocket separating during the launch was released. For missions involving national security interests, secrecy of this kind is routine procedure.
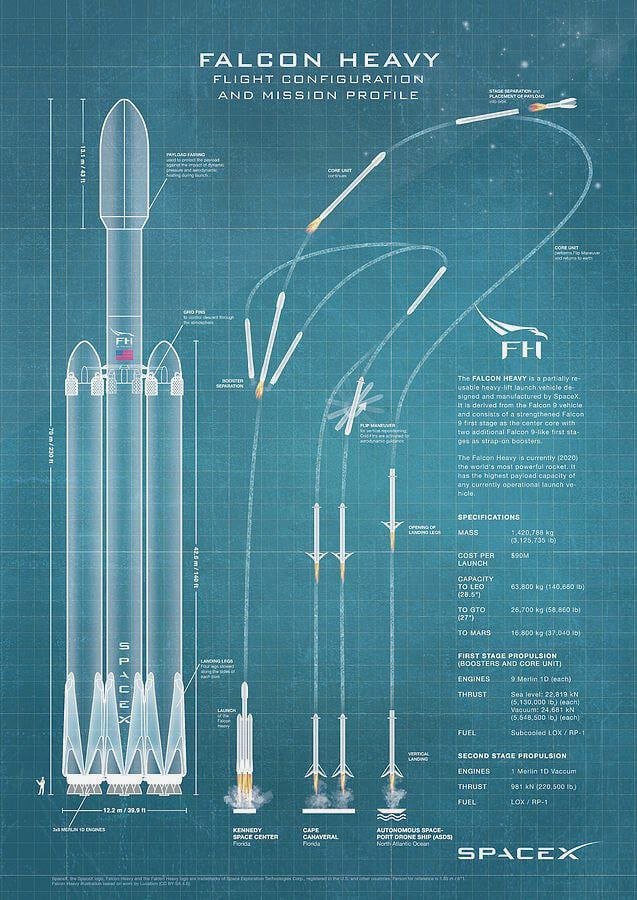
US Spy Satellites Falcon9:
The successful landing of the first stage of the Falcon 9 rocket after its launch, which occurred around six minutes prior. The first stage of the Falcon 9 rocket performed an entry burn to slow down and facilitate its controlled descent back to Earth. After this, it landed on a drone ship named “Of Course I Still Love You,” which was stationed in the Pacific Ocean.
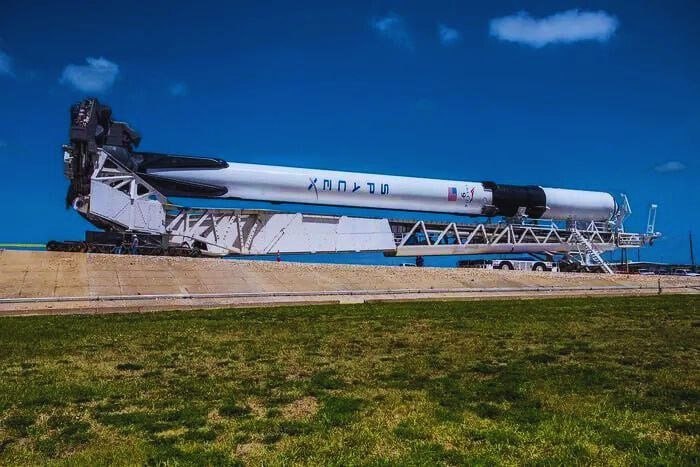

It’s noteworthy that this particular landing marked the 16th successful launch and landing for this specific Falcon 9 first stage rocket, showcasing the reusability aspect of SpaceX’s technology.
NRO Mission, NROL-146:
The mission description provided by the National Reconnaissance Office (NRO), stating that NROL-146 will be the first launch of NRO’s proliferated architecture. The NRO explains that this architecture emphasizes “Strength in Numbers,” suggesting a strategy that likely involves deploying multiple satellites to enhance the effectiveness and resilience of the reconnaissance capabilities. The specifics of this architecture remain undisclosed, consistent with the NRO’s tendency to keep operational details classified.
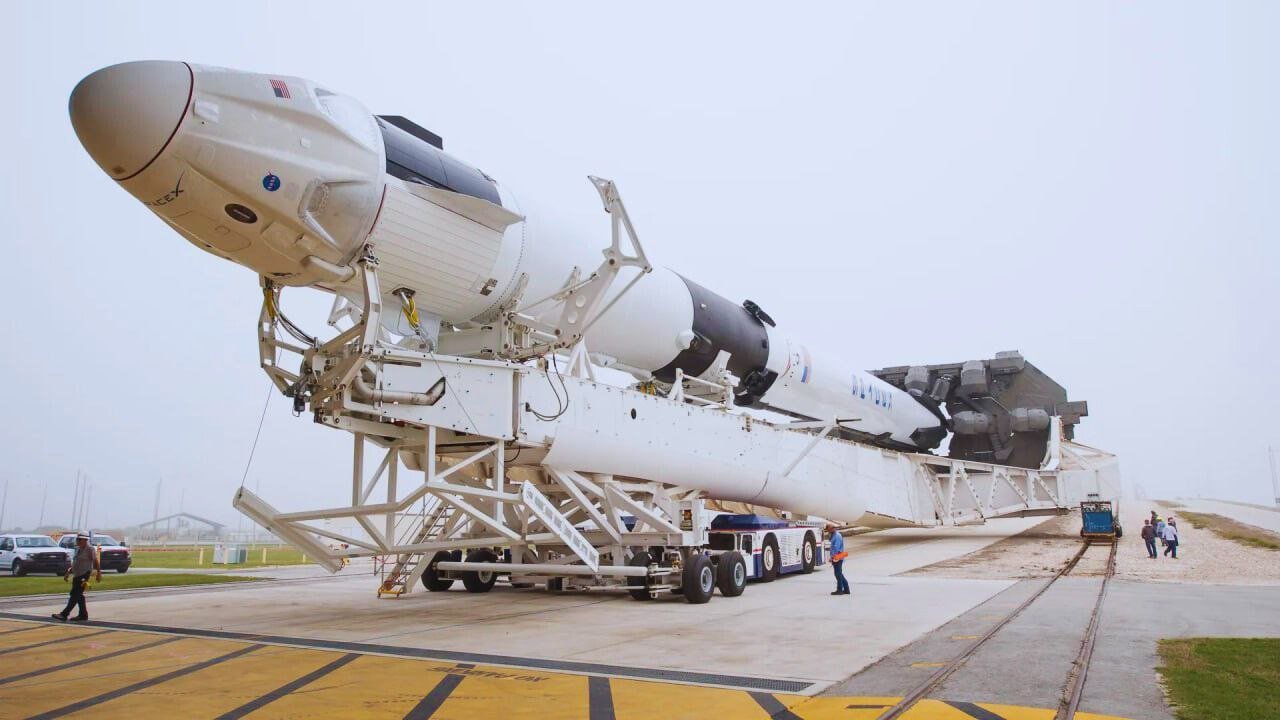

The National Reconnaissance Office (NRO) adopting a new strategy for its satellite architecture, termed a “proliferated overhead architecture.” This strategy involves deploying numerous smaller satellites instead of relying on a few large and bulky spacecraft. The smaller satellites are designed to offer enhanced capability and resilience.
This new strategy, it’s reasonable to assume that the NROL-146 mission likely involved the launch of multiple small satellites rather than a single large spacecraft. This approach aligns with the NRO’s emphasis on deploying a constellation of smaller satellites to achieve its reconnaissance objectives. By launching multiple smaller satellites, the NRO can potentially increase coverage, flexibility, and resilience in its operations.
OUR SITE: TOINEWSALERT.COM
USA Spy Satellites:
The important launch of a series of espionage satellites for the US government by SpaceX, a private aircraft manufacturer and space transportation business. Early on Wednesday morning, the Vandenberg Space Force Base in California conducted the launch. The National spy Office (NRO), which is in charge of running US spy satellites, carried out the operation, designated NROL-146.
Space X Technology:
About the particular payloads that the NROL-146 mission is carrying, not much is known. This lack of detail is typical of NRO missions, as the organisation prefers to keep the actions and capabilities of its satellites secret. As a result, no film of the stages of the Falcon 9 rocket separating during the launch was released. For missions involving national security interests, secrecy of this kind is routine procedure.
The successful landing of the first stage of the Falcon 9 rocket after its launch, which occurred around six minutes prior. The first stage of the Falcon 9 rocket performed an entry burn to slow down and facilitate its controlled descent back to Earth. After this, it landed on a drone ship named “Of Course I Still Love You,” which was stationed in the Pacific Ocean.
It’s noteworthy that this particular landing marked the 16th successful launch and landing for this specific Falcon 9 first stage rocket, showcasing the reusability aspect of SpaceX’s technology.
The mission description provided by the National Reconnaissance Office (NRO), stating that NROL-146 will be the first launch of NRO’s proliferated architecture. The NRO explains that this architecture emphasizes “Strength in Numbers,” suggesting a strategy that likely involves deploying multiple satellites to enhance the effectiveness and resilience of the reconnaissance capabilities. The specifics of this architecture remain undisclosed, consistent with the NRO’s tendency to keep operational details classified.
The National Reconnaissance Office (NRO) adopting a new strategy for its satellite architecture, termed a “proliferated overhead architecture.” This strategy involves deploying numerous smaller satellites instead of relying on a few large and bulky spacecraft. The smaller satellites are designed to offer enhanced capability and resilience.
This new strategy, it’s reasonable to assume that the NROL-146 mission likely involved the launch of multiple small satellites rather than a single large spacecraft. This approach aligns with the NRO’s emphasis on deploying a constellation of smaller satellites to achieve its reconnaissance objectives. By launching multiple smaller satellites, the NRO can potentially increase coverage, flexibility, and resilience in its operations.
Scientists had predicted that the Antarctic’s Doomsday Glacier would melt more quickly than it is. 2:
Scientists had predicted that the Antarctic’s Doomsday Glacier would melt more quickly than it is. 2
The Next Ninja Theory Game Is Supposedly Already Greenlit, Hellblade02:
The Next Ninja Theory Game Is Supposedly Already Greenlit, Hellblade02
Acer introduces the Swift 14 AI laptop, a strong AI-powered work tool:
Acer introduces the Swift 14 AI laptop, a strong AI-powered work tool.
