Contents
Introduction to the Loggerhead Sea Turtle
The loggerhead sea turtle, scientifically known as Caretta caretta, is a remarkable marine species recognized for its distinctive large head and robust jaw structure. These turtles typically measure between 2.5 to 3.5 feet in length and can weigh up to 400 pounds, with some individuals even surpassing this weight. Their carapace, or shell, is heart-shaped and adorned with a reddish-brown coloration, which aids in their identification. Loggerheads are predominantly found in subtropical and temperate regions of the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian Oceans, preferring coastal bays, estuaries, and shallow waters for nesting and feeding.
Loggerhead sea turtles play a vital role in maintaining the health of marine ecosystems. As omnivores, they feed on a variety of prey including crustaceans, mollusks, and jellyfish, contributing to the balance of these populations. Additionally, their nesting activities help to nourish beach ecosystems; the nutrients from their unhatched eggs provide essential sustenance for dune vegetation, which in turn stabilizes the shoreline and provides habitat for other species.
Despite their ecological importance, loggerhead sea turtles are currently listed as vulnerable on the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List. They face numerous threats, including habitat loss due to coastal development, accidental capture in fishing gear, pollution, and climate change. These challenges have led to significant declines in their populations, making conservation efforts increasingly critical.
Rehabilitation of injured or sick loggerhead sea turtles is a crucial component of conservation strategies. Facilities dedicated to marine life rescue and rehabilitation provide essential medical care and a safe environment for recovery. Successful rehabilitation and subsequent release of these turtles back into the wild not only enhance individual survival rates but also contribute to the overall stability of their populations. Such efforts are instrumental in ensuring that loggerheads continue to thrive and perform their essential roles within marine ecosystems.
The Rescue and Rehabilitation Journey of Loggerhead Sea Turtle Returns to Atlantic Ocean
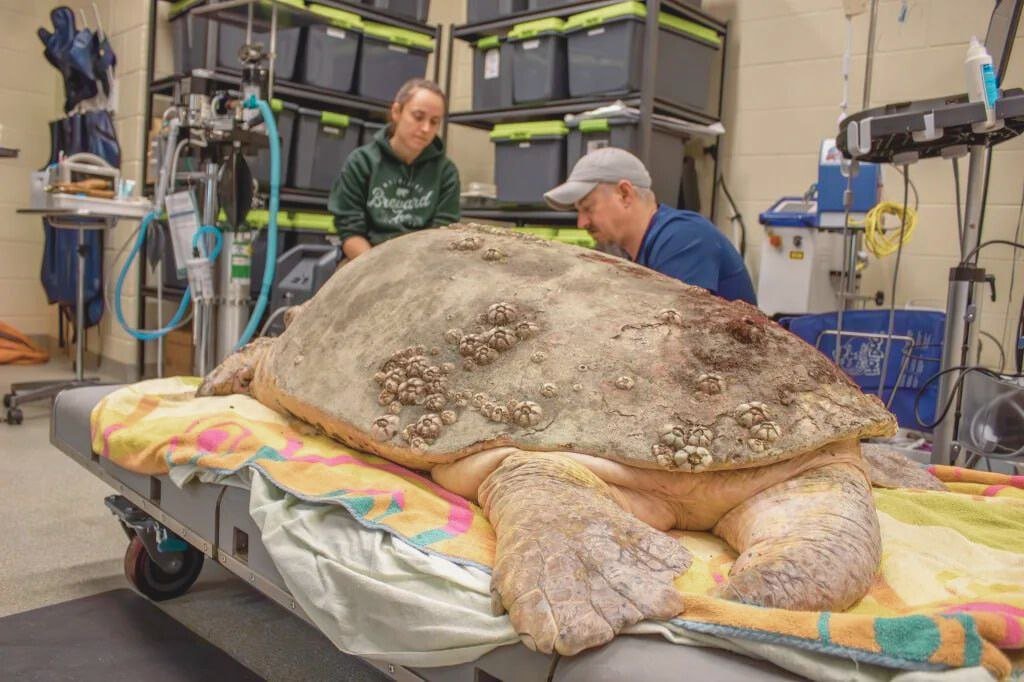
In a remarkable rescue operation, a 375-pound loggerhead sea turtle was found stranded on a Florida beach, exhibiting signs of severe distress and malnutrition. The turtle, later named “Neptune” by rescuers, was in a critical state, suffering from multiple health issues including dehydration, shell damage, and a severe case of intestinal blockage caused by ingesting marine debris.
Upon arrival at the rehabilitation center, Neptune underwent a comprehensive medical evaluation conducted by a team of experienced veterinarians and marine biologists. The initial assessment revealed that the turtle’s condition was precarious, necessitating immediate intervention. The primary concerns were its weakened state and the substantial internal blockages compromising its digestive system.
The rehabilitation process for Neptune was intensive and multifaceted, involving a combination of medical treatments, specialized diet plans, and ongoing care. The veterinarians administered fluids to rehydrate the turtle and prescribed antibiotics to prevent infections. A painstaking procedure was conducted to remove the ingested debris, which posed a significant risk to Neptune’s health.
Dietary management played a crucial role in the turtle’s recovery. Neptune was gradually introduced to a nutrient-rich diet tailored to its specific needs, consisting of a variety of seafood and vitamin supplements to restore its strength. The care regimen also included physical therapy to address the muscle atrophy resulting from the turtle’s extended period of inactivity.
The rehabilitation journey was a collective effort, with marine biologists closely monitoring Neptune’s progress and volunteers providing essential support. The volunteers contributed to daily feeding, cleaning the holding tanks, and assisting with medical procedures under the guidance of the veterinary team. Their dedication and coordinated efforts were instrumental in Neptune’s recovery.
After three months of consistent and meticulous care, Neptune showed significant improvement. It regained its strength, with its health indicators returning to normal ranges. The successful rehabilitation of Neptune is a testament to the collaborative efforts of the veterinarians, marine biologists, and volunteers, highlighting the importance of such initiatives in marine wildlife conservation.
The Release Back into the Atlantic Ocean
The release of the 375-pound loggerhead sea turtle back into the Atlantic Ocean marked a significant milestone for both the rehabilitation team and conservationists. After three months of intensive care at the Florida Marine Life Center, the turtle’s return to its natural habitat was met with excitement and relief. The preparation for this momentous event involved meticulous planning and coordination. The team ensured that the turtle was in optimal health, conducting thorough check-ups and monitoring its progress closely.
On the day of the release, the transportation process was handled with utmost care. The turtle was securely transported in a specialized vehicle, ensuring minimal stress and maximum comfort during the journey. Upon arrival at the designated release site, the atmosphere was charged with anticipation. Conservationists, volunteers, and local officials gathered to witness this triumphant moment. Dr. Sarah Thompson, the lead marine biologist at the center, expressed her elation, stating, “Seeing this magnificent creature return to the ocean is a testament to the hard work and dedication of our team. It’s moments like these that remind us why we do what we do.”
As the turtle was gently lowered into the water, there was a collective sense of accomplishment. The loggerhead paused momentarily, as if acclimating to the familiar surroundings, before gracefully swimming away. The sight was both emotional and inspiring, symbolizing a successful recovery and the promise of a hopeful future. The attending officials emphasized the importance of such conservation efforts, with Mayor John Davidson highlighting, “This release underscores our commitment to preserving marine life and protecting our oceans. It’s a proud day for our community.”
The turtle’s initial reaction upon returning to its natural habitat was a reassuring sight for the rehabilitation team. Its confident and steady movements affirmed that the months of care and rehabilitation had indeed prepared it for a successful reintegration into the wild. This event not only celebrated the turtle’s journey but also reinforced the significance of continued conservation efforts to protect and preserve marine species.
The successful rehabilitation and release of the 375-pound loggerhead sea turtle underscore the broader implications for sea turtle conservation efforts. Each individual success story, like this one, plays a crucial role in the larger mission to protect and preserve loggerhead sea turtles, which are listed as a vulnerable species by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). This particular case highlights the importance of dedicated conservation programs that focus not only on rescuing and rehabilitating injured or sick sea turtles but also on ensuring their safe return to their natural habitats.
Ongoing conservation programs are instrumental in maintaining the delicate balance of marine ecosystems. Organizations such as the Sea Turtle Conservancy and local Florida-based initiatives work tirelessly to monitor nesting sites, protect eggs from predators, and reduce threats from human activities. These programs often involve tagging and tracking released turtles to gather data on their migration patterns, which is vital for understanding and mitigating the challenges they face in the wild.
Public awareness campaigns are equally significant in fostering a culture of conservation. Educational programs, community engagement activities, and social media initiatives aim to inform the public about the importance of sea turtles to marine ecosystems. By highlighting success stories like the release of this loggerhead turtle, these campaigns can inspire individuals to take action, whether through volunteering, supporting conservation organizations, or adopting eco-friendly practices that reduce pollution and habitat destruction.
The public can support these efforts by participating in beach clean-ups, reducing plastic use, and adhering to guidelines that protect marine life, such as keeping beaches dark during nesting season to avoid disorienting hatchlings. Financial contributions to conservation organizations also provide essential resources for rescue and rehabilitation operations.
With continued dedication to these multifaceted conservation efforts, there is a hopeful outlook for the future of loggerhead sea turtles and marine conservation as a whole. Collaborative efforts between scientists, conservationists, and the public are paving the way for a sustainable future where sea turtles can thrive in their natural environments.
OUR SITE: toinewsalert.com
