Contents

Introduction to Mpox and Its Global Impact
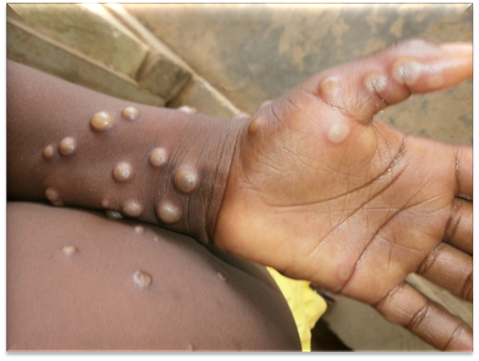
Mpox, also known as Monkeypox, is a zoonotic viral disease originating from wild animals, primarily rodents and primates. First identified in humans in the 1970s, Mpox is caused by the Monkeypox virus, a member of the Orthopoxvirus genus. The disease presents with symptoms similar to smallpox, including fever, headache, muscle aches, and a characteristic rash that progresses from macules to pustules. Although less lethal than smallpox, Mpox can lead to severe complications, especially in immunocompromised individuals and children.
Transmission of Mpox occurs through direct contact with the blood, bodily fluids, or cutaneous or mucosal lesions of infected animals. Human-to-human transmission, though less common, can happen via respiratory droplets during prolonged face-to-face contact, or through fomites, such as contaminated clothing or bedding. The disease’s incubation period ranges from 5 to 21 days, making early detection and isolation critical in curbing its spread.
Globally, Mpox has had a significant impact, particularly in West and Central Africa where the disease is endemic. However, sporadic outbreaks have been reported in other regions, facilitated by global travel and trade. The socioeconomic consequences of Mpox outbreaks are profound, straining healthcare systems, disrupting local economies, and exacerbating existing public health challenges. In affected regions, the disease has led to increased healthcare costs, loss of productivity, and heightened public fear and stigma.

The urgent need for a strategic framework to combat Mpox effectively cannot be overstated. Recent outbreaks have underscored the necessity for a coordinated global response to enhance prevention, surveillance, and control measures. The World Health Organization’s newly released strategic framework aims to address these needs by providing comprehensive guidelines for countries to strengthen their public health capabilities, improve disease detection and reporting, and implement effective intervention strategies. This proactive approach is essential to mitigate the impact of Mpox and safeguard global health security.
WHO’s Role in Global Health
The World Health Organization (WHO) plays a pivotal role in global health by spearheading initiatives that aim to improve health outcomes across the world. Established in 1948, WHO’s mission is to promote health, keep the world safe, and serve the vulnerable. As the directing and coordinating authority on international health within the United Nations system, WHO collaborates with a myriad of stakeholders, including international governments, health organizations, and non-governmental organizations to tackle health crises and enhance public health systems.
WHO’s collaboration with various entities is instrumental in addressing health challenges. By fostering partnerships, WHO ensures a unified and comprehensive approach to health issues. The organization’s efforts in combating diseases are exemplified through its success in managing outbreaks and health emergencies. For instance, WHO’s response to the Ebola crisis in West Africa in 2014-2016 involved coordinating with governments, deploying health professionals, and mobilizing resources to control and eventually contain the epidemic. This multi-faceted response not only curbed the spread of the disease but also highlighted the importance of international cooperation in managing health crises.

Moreover, WHO’s role extends beyond emergency response. The organization is also involved in setting standards and guidelines, providing technical support, and monitoring global health trends. Through initiatives such as the Global Health Security Agenda (GHSA) and the International Health Regulations (IHR), WHO works to strengthen countries’ capacities to prevent, detect, and respond to health threats. These frameworks are designed to foster preparedness and resilience, ensuring that nations are better equipped to handle future health emergencies.
In its ongoing efforts, WHO remains committed to addressing a wide range of health issues, from infectious diseases to non-communicable diseases, mental health, and health system strengthening. The organization’s comprehensive approach and its ability to mobilize a global response are critical in safeguarding public health and advancing global health security.
Development of the Strategic Framework
The development of the World Health Organization’s (WHO) strategic framework for enhancing the prevention and control of Mpox was a comprehensive and meticulous process. It began with extensive research aimed at understanding the epidemiology and transmission dynamics of Mpox. This foundational research provided the necessary insights into how the disease spreads, its impact on various populations, and the existing gaps in current prevention and control measures.

Following the research phase, WHO engaged in a series of consultations with a wide array of stakeholders. These consultations included public health experts, epidemiologists, virologists, and representatives from affected communities. Their input was invaluable in ensuring that the framework would be both scientifically robust and practically applicable. The inclusion of diverse perspectives helped in identifying the unique challenges faced by different regions and populations, thereby fostering a more inclusive and equitable approach to Mpox prevention and control.
Expert inputs played a pivotal role in shaping the strategic framework. Specialists in infectious diseases, public health policy, and healthcare delivery contributed their knowledge and experience, ensuring that the framework was grounded in the latest scientific evidence and best practices. These experts helped to refine the objectives and goals, making sure they were both ambitious and achievable.
The key objectives of the WHO strategic framework are centered on four main goals: improving surveillance and detection, enhancing public awareness and education, strengthening healthcare systems, and fostering international collaboration. Improving surveillance and detection involves developing more efficient and accurate diagnostic tools and protocols. Enhancing public awareness aims to educate communities about Mpox transmission and prevention methods. Strengthening healthcare systems focuses on ensuring that healthcare providers are well-equipped and trained to manage Mpox cases. Lastly, fostering international collaboration seeks to build a coordinated global response to Mpox, leveraging resources and expertise from across the world.
In summary, the development of the strategic framework was a multi-faceted effort that combined rigorous research, stakeholder consultations, and expert inputs. The resulting framework sets forth clear and actionable objectives that aim to significantly bolster the global response to Mpox.
The World Health Organization (WHO) has introduced a comprehensive strategic framework aimed at enhancing the prevention and control of Mpox. This framework is built around four pivotal components: surveillance systems, vaccination programs, public health education, and emergency response strategies. Each of these elements plays a crucial role in mitigating the spread of Mpox and fostering a robust public health infrastructure.
Surveillance Systems
Effective surveillance systems are the cornerstone of the strategic framework. They are designed to provide real-time data on Mpox cases, enabling rapid identification and response to outbreaks. These systems integrate various data sources, including clinical reports, laboratory results, and epidemiological investigations, to track the disease’s spread and evolution. By enhancing data collection and analysis, the WHO aims to improve the accuracy of outbreak predictions and tailor interventions more precisely.
Vaccination Programs
Vaccination programs are another critical component of the framework. They focus on increasing the immunization coverage among high-risk populations and ensuring the availability of vaccines during outbreaks. The strategic framework emphasizes the importance of developing and distributing effective vaccines, alongside implementing rigorous monitoring to evaluate vaccine efficacy and safety. By fortifying vaccination efforts, the WHO seeks to build herd immunity and reduce the incidence of Mpox.
Public Health Education
Public health education is essential for raising awareness about Mpox and promoting preventive behaviors. The framework outlines strategies for disseminating accurate information about the disease, its transmission, and preventive measures. This includes educational campaigns targeting both the general public and healthcare professionals. By enhancing public knowledge and engagement, the WHO aims to foster a community-wide commitment to Mpox prevention and control.
Emergency Response Strategies
Emergency response strategies are designed to ensure a swift and coordinated reaction to Mpox outbreaks. These strategies involve the development of contingency plans, the establishment of rapid response teams, and the creation of stockpiles of essential medical supplies. The framework also underscores the importance of international cooperation and resource-sharing to manage cross-border outbreaks effectively. By strengthening emergency preparedness, the WHO aims to minimize the impact of Mpox outbreaks and safeguard public health.
Implementation Strategies
The implementation of the WHO’s strategic framework for enhancing the prevention and control of Mpox requires concerted efforts at both national and international levels. To ensure the framework’s success, it is imperative for countries to adapt the guidelines to their specific needs and contexts. This involves a detailed assessment of the local epidemiological landscape, healthcare infrastructure, and available resources. Tailoring the framework to align with these factors will enable more effective and sustainable interventions.
At the national level, health ministries play a pivotal role in driving the implementation process. They are responsible for formulating policies, allocating resources, and coordinating with various stakeholders. Health ministries must also prioritize capacity building by providing training to healthcare workers on Mpox prevention, diagnosis, and treatment. This is essential for fostering a well-prepared and responsive healthcare system.
Local governments are equally critical in the implementation of the framework. They are tasked with executing national policies on the ground, ensuring that interventions reach communities effectively. Local governments should engage with community leaders and organizations to promote awareness and acceptance of Mpox control measures. Additionally, they need to facilitate access to healthcare services, particularly in underserved areas, to ensure comprehensive coverage.
International partners, including non-governmental organizations (NGOs), research institutions, and funding agencies, also play a significant role in the implementation process. These partners can provide technical expertise, financial support, and innovative solutions to bolster national efforts. Collaboration with international partners enables the sharing of best practices and lessons learned, which can enhance the overall effectiveness of Mpox control strategies.
In conclusion, the successful implementation of the WHO’s strategic framework for Mpox prevention and control hinges on the collective efforts of health ministries, local governments, and international partners. By adapting the framework to local contexts and fostering collaboration across all levels, countries can effectively mitigate the impact of Mpox and safeguard public health.
The successful implementation of the WHO’s strategic framework for enhancing prevention and control of Mpox faces numerous challenges and barriers. One of the most significant challenges is the limited resources available in many regions. Financial constraints can significantly hamper the ability to deploy necessary interventions, conduct extensive research, and support public health infrastructures. Without adequate funding, even the most well-designed strategies can falter.
Logistical difficulties also pose a considerable barrier to effective Mpox control. In many areas, especially those with underdeveloped infrastructure, distributing medical supplies and vaccines can be a complex and resource-intensive process. Remote and rural regions may lack the necessary facilities to store vaccines at required temperatures, complicating the delivery and maintenance of an effective vaccination program. Additionally, the uneven distribution of healthcare facilities can lead to disparities in access to Mpox prevention and treatment services.
Vaccine distribution represents another critical challenge. Ensuring that vaccines reach all segments of the population, particularly those in underserved and high-risk communities, is a daunting task. Issues such as vaccine hesitancy, misinformation, and distrust in medical institutions can further hinder the success of vaccination campaigns. Public resistance, fueled by misinformation and cultural beliefs, can lead to lower vaccination rates, thereby reducing herd immunity and increasing the risk of Mpox outbreaks.
Moreover, addressing these challenges requires a concerted effort to enhance public awareness and education regarding Mpox. Effective communication strategies are essential to counteract misinformation and build trust within communities. Public health campaigns must be culturally sensitive and inclusive, ensuring that accurate information reaches diverse populations.
To ensure the framework’s effectiveness, it is imperative to address these challenges proactively. This involves securing adequate funding, improving logistical capabilities, ensuring equitable vaccine distribution, and fostering public trust through transparent and inclusive communication strategies. By overcoming these barriers, the WHO’s strategic framework can achieve its goal of enhancing Mpox prevention and control on a global scale.
Monitoring and Evaluation
The World Health Organization’s strategic framework for the prevention and control of Mpox is underpinned by robust mechanisms for monitoring and evaluation. Effective monitoring and evaluation are essential to ensure that the implemented strategies are achieving their intended outcomes and to make necessary adjustments in a timely manner.
Key performance indicators (KPIs) serve as the cornerstone for assessing the progress of the strategic framework. These KPIs include metrics such as the incidence and prevalence of Mpox, vaccination coverage rates, and the speed of outbreak response. Collecting and analyzing these indicators allows for an evidence-based understanding of the framework’s impact on public health.
Data collection methods are meticulously designed to gather comprehensive and accurate information. These methods encompass both passive and active surveillance systems. Passive surveillance involves the routine reporting of Mpox cases by healthcare facilities, while active surveillance entails proactive efforts to identify new cases through field investigations and community engagement. Additionally, laboratory data, hospital records, and epidemiological studies contribute to a holistic view of the disease’s dynamics.
The reporting process is structured to ensure transparency and accountability. Regular reports are generated and disseminated to key stakeholders, including public health officials, healthcare providers, and international partners. These reports highlight the current status of Mpox, identify emerging trends, and provide actionable insights. Furthermore, periodic reviews and evaluations are conducted to assess the overall effectiveness of the framework and to identify areas for improvement.
Continual assessment is emphasized to adapt and enhance strategies as new information and technologies become available. By fostering a culture of continuous improvement, the WHO aims to maintain a dynamic and responsive approach to Mpox prevention and control. This iterative process ensures that the strategic framework remains relevant and effective in addressing the evolving challenges posed by Mpox.
Future Directions and Conclusion
As the World Health Organization (WHO) continues to spearhead efforts to combat Mpox, future directions will play a critical role in enhancing prevention and control measures. The landscape of medical research is rapidly evolving, offering potential breakthroughs in understanding Mpox’s virology and epidemiology. Advanced molecular techniques and genomic studies could pave the way for more effective vaccines and targeted therapies, reducing the disease’s burden on affected populations.
Technology, too, stands to revolutionize Mpox control strategies. Digital health tools, such as mobile health applications and telemedicine, can facilitate timely diagnosis and treatment, especially in remote and resource-limited settings. Real-time data analytics and artificial intelligence can provide predictive insights, enabling proactive measures and swift response to emerging outbreaks.
International cooperation remains a cornerstone of the strategic framework for Mpox prevention and control. Collaborative efforts among countries, international organizations, and non-governmental organizations are essential for sharing knowledge, resources, and best practices. Strengthening health systems and ensuring equitable access to healthcare services and vaccines will be vital in achieving global Mpox control.
The WHO’s strategic framework emphasizes the importance of a coordinated and comprehensive approach. By integrating advancements in medical research, leveraging technology, and fostering international cooperation, the global community can effectively mitigate the impact of Mpox. It is crucial to maintain momentum and prioritize investment in Mpox research and public health infrastructure.
In conclusion, the strategic framework set forth by WHO serves as a pivotal guide for future Mpox prevention and control efforts. The collective commitment of nations and stakeholders is imperative to address the challenges posed by Mpox. By working together, we can safeguard public health and move towards a world where Mpox is no longer a significant threat.
OUR SITE: toinewsalert.com
Fish Oil Supplements May Raise Risk of Stroke and Heart Issues: Study Suggests
Fish Oil Supplements May Raise Risk of Stroke and Heart Issues: Study Suggests
Tornado Strikes Fort Campbell: Power Outages and Damage in Hopkinsville, Kentucky
Tornado Strikes Fort Campbell: Power Outages and Damage in Hopkinsville, Kentucky





